
A survey that allows children to respond to questions about climate change is the best option. These surveys use a variety of methods, including interviews and focus groups, to measure kids' interest in science. These surveys have produced remarkable results over the last decade.
Surveys have shown that people who care about climate issues are more likely to see negative impacts from climate change, believe that the effects of climate change are more likely to be mitigated, and have a more optimistic view of how climate scientists work. They also are more likely to believe that proposed solutions to climate change will be effective.
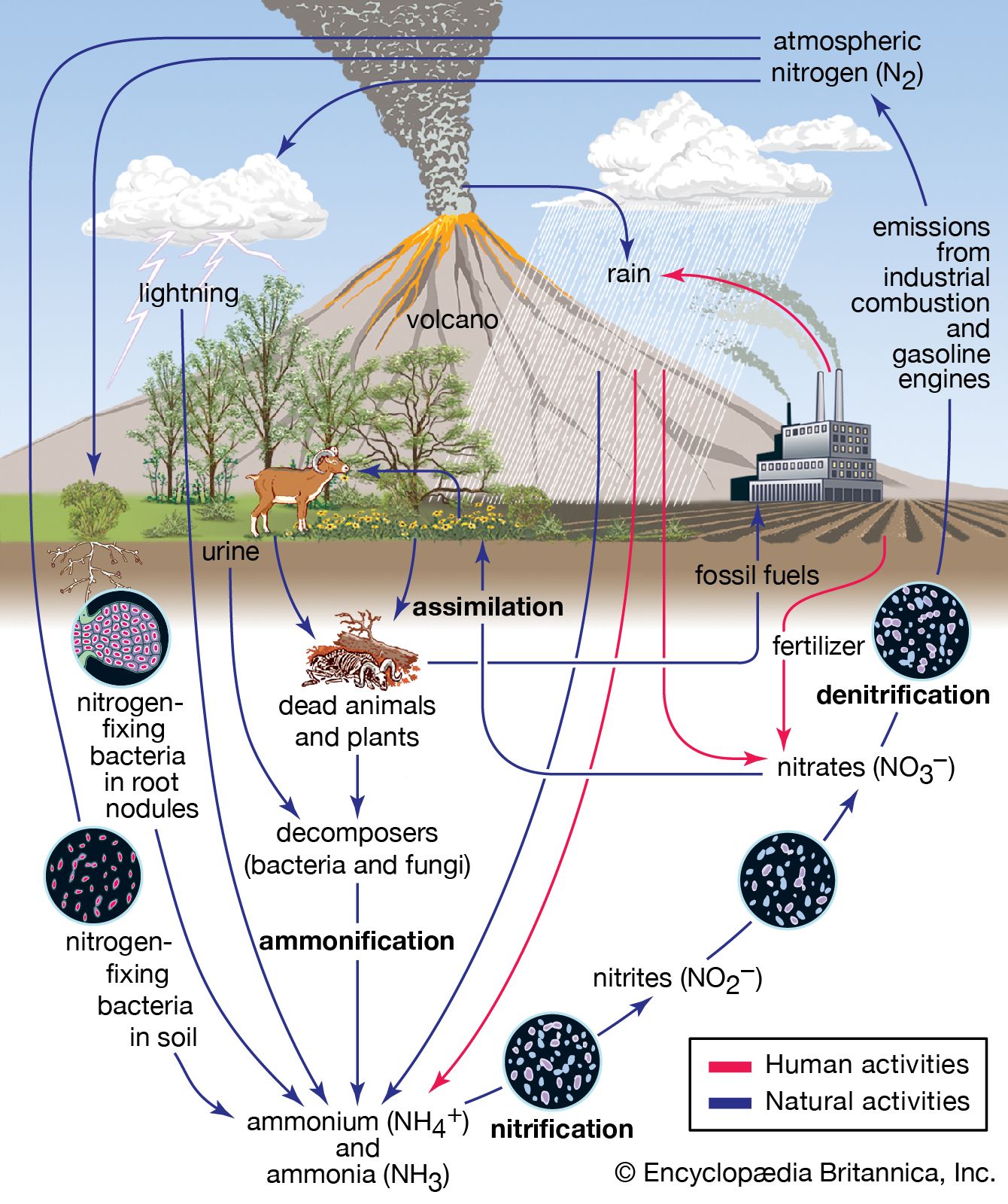
There are three types. One is concerned with whether the climate is altering; another concerns whether it is being caused by human activity; and the final is concerned about how bad the climate may be. Some questions explicitly expressed scepticism about the existence of climate change, and some asked for proof that the climate is changing. In addition to asking participants to make statements about how they would act, many of these surveys asked about the nature of the phenomenon and the causes of climate change.
Answers to these questions reveal the rich and varied views that children have about climate change. Children frequently use science-fiction themes as well as speculative language when responding to these questions. Although it is clear that some people have an understanding of climate change, this also means that others may be creating incorrect theories.
Participants were quick to link the worst things about climate change with the terrible events shown in movies and videos. However, they were not able to link the future consequences of climate change with the future effects of human-caused or non-human-caused climate change. This results suggests that participants are making inaccurate predictions about climate change. If these ideas are not addressed they could continue indefinitely.
Others used scientific terminology and more speculation to describe future climate change impacts. Participants were asked to envision the consequences of climate change in the distant future, and to think about the impacts of climate change on humans and animals in the future.
This category included questions about the geographic location of climate-related impacts and the timing and magnitude of those changes. One question asked participants for an estimate of the impact climate change will have on the United Kingdom. Another question asked about impacts of climate changes on the food- and agriculture industries.
The most common type of climate change questions were those that addressed the nature of the phenomenon. The first category of climate questions was those that asked about the causes of climate changes, the current state and future effects on human health. With the exception of a few questions that were more specific and general, most of these questions were very broad.
FAQ
What is the climate change's impact on ecosystems and biodiversity?
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. Changes in the hydrological cycles can also have an impact on water availability for species that live in aquatic environments.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. Up to 30% of all animal species could be extinct by 2050 due to climate change, which would lead to further losses in ecological communities.
Climate change poses a significant threat to biodiversity and human societies, as well as to ecosystems that provide food, water, timber, or other services. To mitigate its effect efforts must be made at all levels to reduce global warming trends and future damages should be avoided where possible with careful management practices.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Climate change is directly affected by land use changes and deforestation. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
Changes in land usage can also cause more greenhouse gasses to be released into the atmosphere. When forests are cleared for livestock production, the use of fertilizer and pesticides may lead to an increase in methane or nitrous oxide emissions. Also, clearing can increase soils containing large amounts of carbon; these soils may be exposed to farming activities that turn them over or disturb them, which will release more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
Conclusion: Deforestation, land-use changes and other factors have significantly contributed to global warming. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
How can developing countries and communities cope with the effects of climate changes?
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause decreased crop yields. This will have a significant impact on poorer communities suffering from food insecurity. Extreme weather events such as hurricanes or heatwaves may cause damage to infrastructure and the displacement of people. This can further perpetuate economic inequality.
The long-term implications of climate change include continued resource scarcity, poverty, and health impacts including an increased number of vector-borne diseases such as malaria or dengue fever. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
What's the current climate in the world? And how does it change?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes are already having a profound impact on ecosystems around the world, causing extinctions and disruption of habitats. They are also threatening the lives and livelihoods of billions of people, particularly those in areas already facing resource scarcity and poverty.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also contributing to existing social inequalities. Itdisproportionately affects marginalized communities, which lack the resources and knowledge required to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
How can climate change be mitigated or reduced in its impact?
There are many things you can do to lessen and mitigate the consequences of climate changes. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions through better energy practices and using alternative sources of energy such as renewable resources, employing more efficient agricultural techniques, improving land management practices, enhancing air quality laws, protecting forests and wilderness habitats, protecting against extreme weather events such as floods and droughts, investing in sustainable transport systems, strengthening early warning systems for disasters, beginning a research program on the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems, investing in green technologies such as solar panels or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consumption habits, implementing suitable environmental regulations across all sectors of society. It's also important to educate the public about climate change. This will encourage people to be responsible for their actions.
What impact does climate change have on food security and agriculture?
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. Changes in climate can have an impact on rainfall patterns, temperature, soil moisture, extreme weather, and other aspects of agriculture. This can affect farming activities and reduce crop yields. It can also lead to a decrease in agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures may lead to an increase in pests and diseases that can affect crops. They can also result in shifts of ranges suitable to agricultural production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Global warming and climate change are complex issues. However, governments around the world are making efforts to reduce these effects through adaptation strategies such as climate-smart agricultural (CSA) strategic investments. This involves the promotion of sustainable methods such crop rotation techniques, or the conservation and preservation of native seeds varieties. These are ways to help mitigate the negative effects of climate change. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. It is essential to create sustainable solutions that adhere to the international guidelines for quality nutrition in our changing climates. This requires collaboration between all stakeholders, from government agencies at an international level to local NGOs.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to support climate-friendly policies and companies
There are many ways that individuals can support climate-friendly companies and policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also immediately take more practical steps such as switching providers when possible to ones that have a better environmental record or choosing sustainable products over those with higher carbon emissions.
It is important to reduce one's carbon footprint in order to support climate-friendly companies and policies. This may include changing daily habits such unplugging electrical appliances and switching off lights when not required, using environmentally friendly household products like biodegradable cleansers and composting kitchen soiled food scraps rather that putting them in landfills, wearing sustainable fiber clothing, choosing local foods whenever possible, installing energy-efficient energy systems at your home with solar panels or wind turbines, as well as planting trees around the property that absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere.
Investors who are keen to support climate-friendly policies will want to find companies that produce lower carbon emissions before investing. Investors interested in climate-friendly policies should examine their portfolios every so often to make sure they are meeting sustainability standards. Investors may want to ensure that their investments in Green bonds do not finance projects with any activity which contributes more greenhouse gases into the air than they take away. Investors should consider any opportunities that could allow funds to be used for green business activities. These include renewable energy alternatives as a way to promote sustainability and community-building projects using green technologies.