
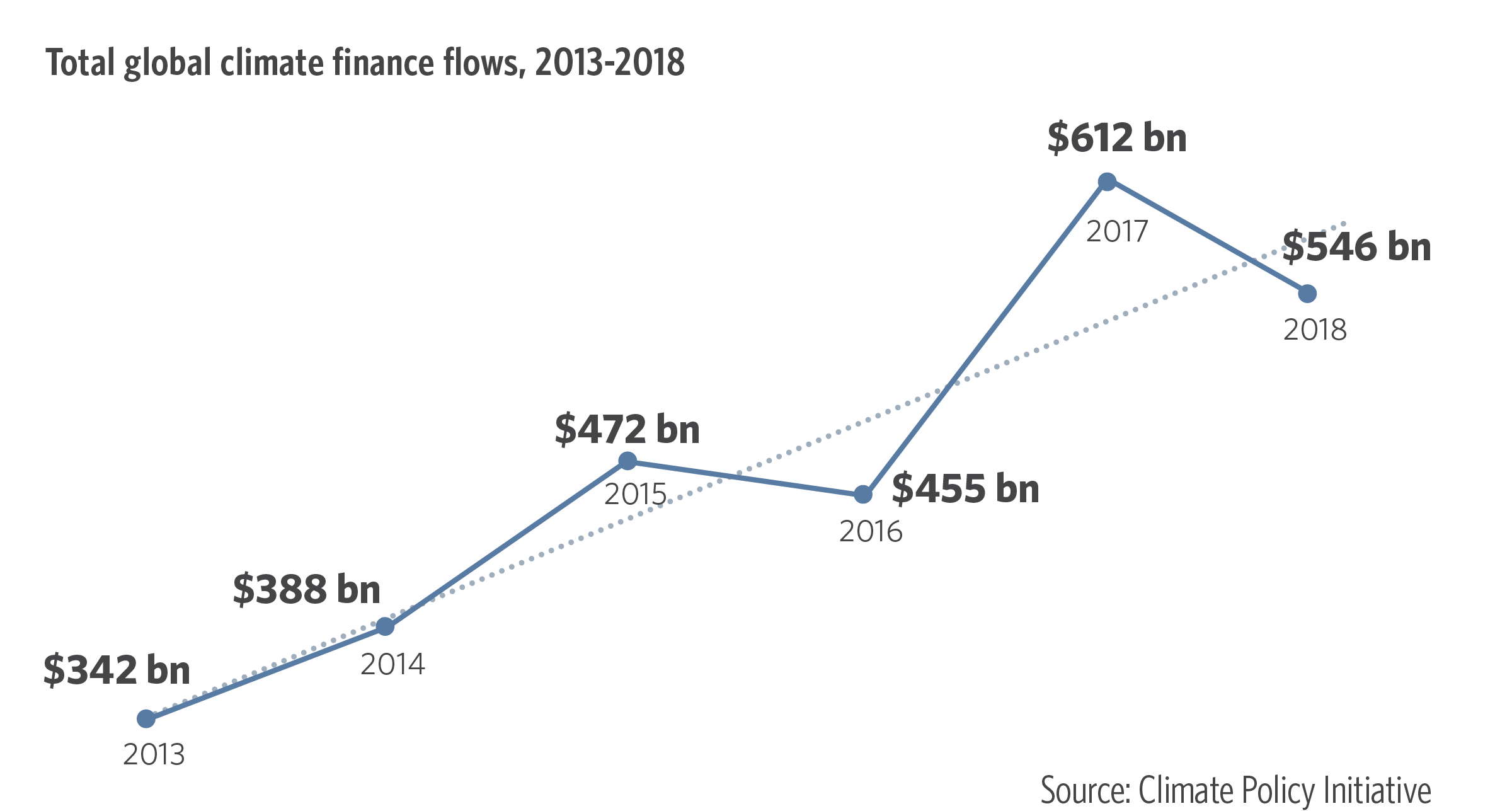
Africa is the most vulnerable continent in terms of Climate Change. As a result, Climate Change financing is important to support climate resilient green economic development. It also funds adaptation and mitigation efforts. These needs can either be met through domestic revenue mobilisation or international private finance. In addition, there is an increasing interest in regional carbon pricing initiatives. These initiatives are being considered by the East African Alliance on Carbon Markets, Climate Finance and Climate Finance.
Sub-Saharan Africa's (SSA) is a region where climate change is especially important. The population is already at high risk of malnutrition. Its rainfed agricultural system is particularly vulnerable to climatic shifts. The region is also experiencing a rise in rural-urban migration, which contributes to its urbanization trend. A large portion of the population in the region relies on ecosystem services. Despite these factors, the SSA is still the continent with the lowest greenhouse gas emissions. This does not address the full effect of Climate Change, which has a negative impact on human existence and natural systems.

Climate change will impact rainfall patterns and storm severity, leading to changes on hydrological regimes and freshwater flow to estuaries. These changes can exacerbate existing anthropogenic pressures. Therefore, adaptation and mitigation must consider both the abiotic effects of Climate Change as compared to the existing anthropogenic pressures. Under a 4 text degree Celsius warming scenario, SSA may experience a sea level increase of up to one meter.
A South African assessment of estuaries' vulnerability to Climate Change is required to inform the development appropriate adaptation strategies and mitigation plans. This study identifies key stressors and potential impacts on estuaries that could be linked to Climate Change.
Climate Change stresses include an increase or decrease in sea level, rainfall, sea ice, and shifts in wind and temperature. These changes will likely impact estuarine processes including nutrient fluxes and biochemical regimes as well as salinity regimes and mouth state. Because of the interaction of land- and sea processes, estuaries have a high degree of dynamic and may vary from one location to another. The spatial resolution of vulnerability assessment must take into consideration topography and the distribution of estuarine, coastal and marine biology.
This study analyzed the future vulnerability of South Africa's estuaries over the near-future (2035-2035), medium-future (1936-2065) as well as the far-future (2066-2099). The data was obtained using statistical models and the Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment. Results showed that an increase in inter-annual variability would lead to a decrease of freshwater runoff to estuaries. Nonetheless, the coastal region of KwaZulu-Natal experienced an increase in extreme precipitation events during the summer.
Numerous studies have been carried out to assess South Africa's vulnerability to climate changes. These studies use statistical models and coastal topography as well as coastal bio-determinants. For this purpose, however, a comprehensive and more detailed consolidated review is necessary.
In addition to providing essential habitat for coastal species, estuaries are also important feeding and nursery grounds for migrant birds. Estuaries also provide excellent habitats for fish and shrimp, as well as other aquatic species.
FAQ
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What is the effect of climate change upon the world's oceans?
Since its inception, climate changes have had significant impacts on the oceans of the world and the marine life that surrounds them. The loss of the ozone coating and constant oceanic temperature increase causes significant disruptions in marine ecosystems.
Climate change also causes unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms. These extreme surges can be deadly for coastal areas. Also, rising temperatures can reduce the oxygen levels in the water system, leading to "deadzones" that are areas with less marine life.
Climate change is also contributing to ocean acidification, caused by excess carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere that accumulates within the oceans. Ocean acidification raises the pH balance which disrupts essential functions of animals unable to adapt such as oysters, clams, and crabs as their shells become weakened.
Higher temperatures can also cause changes in natural habitats. They may shrink or change their geographical location, making it unhabitable for species that depend on them. An increase in ocean stress can accelerate already high extinction rates of many species around the world, resulting in a severe imbalance between predators/prey that could eventually lead to total extinction.
Climate change has ripple effects on entire ecosystems, affecting multiple species directly and indirectly. Evaporation, lowering water volumes, or temperature shifts can all impact sustainable development of fisheries and other maritime activities. Global climate change continues to decimate entire species, changing future lives on earth and below the surface of the oceans.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Climate change and global warming are directly impacting agriculture and food security. The changing climate can impact rainfall patterns and temperatures as well as soil moisture levels. Extreme weather is also possible. This can lead to disruptions in farming activities, lower crop yields, and loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can lead to the proliferation of pests or diseases that affect crops; it can also cause shifts in ranges suitable for agricultural production. In turn, this could increase the cost of food production and result in a greater incidence of hunger and poor nutrition worldwide.
Rising sea levels pose a further threat. They could inundate valuable agricultural land in many coastal areas, leading to higher salinity levels in wetlands, where important crops are grown. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Although the relationship between climate change, global warming, and other factors is complex, there are efforts being made by governments to mitigate them through adaptation strategies. These include strategic investments in climate smart agriculture (CSA), which allows governments around the globe to make strategic investments in adapting their agricultural systems. This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
To ensure food security amidst a rapidly changing environment, it will be essential for farmers around the world to adopt technologies that are more sensitive to changes in the climate when it comes to selecting appropriate crops to grow on certain parcels of land. Improvements must be made within existing infrastructure set-ups so that necessary actions may be taken when critical crop thresholds are hit - this includes introducing stable irrigation networks with adequate access water supplies at times of the year when there is reduced availability due to warmer climates or intense downpours washing away much-needed access water resources outside planting seasons. To truly create lasting solutions that ensure continued adherence to international dietary guidelines regarding quality nutrition within our increasingly variable climates all over the globe - cohesive collaboration between stakeholders ranging from various government administrations at an international level right down to NGOs at local community sites is required.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change can have many impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changing extreme weather events and sea level, as well as an increase in acidity in oceans, are all issues that affect wildlife and ecosystems.
These shifts in climate conditions can cause shifts in habitat areas, disrupt food chains or affect population numbers or species distributions, with potentially dramatic consequences for biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems. The hydrological cycle changes can have an impact on the availability of water for aquatic species.
Moreover, changes to climate result in rising temperatures and more frequent extremes such as droughts and floods which puts more stress on already fragile systems such as coral reefs or tropical rainforests. It is estimated that up to 30% of animal species could become extinct due to climate change by 2050, which would spark a cascade of further losses within ecological communities.
Climate change is a serious threat to biodiversity as well as human societies that rely on functioning ecosystems for food and fresh water. It is essential to mitigate its effects at all levels. Future damages must be avoided by careful management.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to support climate-friendly policies and companies
There are many ways that individuals can support climate-friendly companies and policies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can also immediately take more practical steps such as switching providers when possible to ones that have a better environmental record or choosing sustainable products over those with higher carbon emissions.
Supporting climate-friendly policies and companies is one of the most important steps in reducing one’s carbon footprint. It can be as simple as changing your daily habits like unplugging appliances and turning off lights when they are not needed. You can also use eco-friendly household products such biodegradable cleaners and composting kitchen scraps to reduce carbon emissions.
Investors who wish to support climate-friendly policies need to research companies with lower carbon emission before they invest. Additionally, they should look into their portfolios periodically to ensure they meet the sustainability standards they have set themselves ahead of time. Investors may want to ensure that their investments in Green bonds do not finance projects with any activity which contributes more greenhouse gases into the air than they take away. Investors should also be aware of any opportunities for funds to be used towards green business activities, such as renewable energy alternatives and other initiatives that promote sustainability like community-building projects that use green technologies.