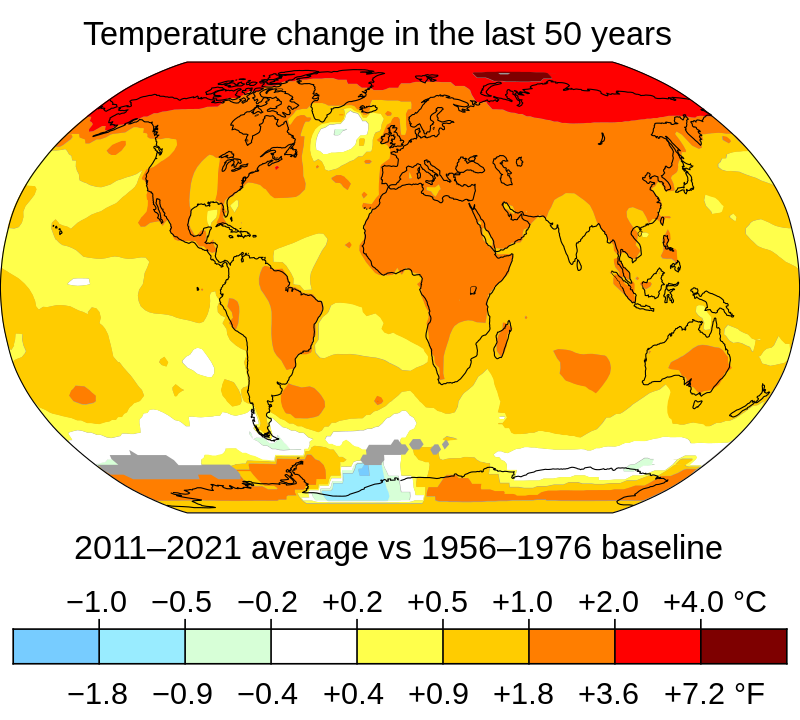
Science and climate are a hot topic. Scientists are unanimous in their belief that human activity is directly responsible for global warming. It is well-known, however, that climate change is primarily caused by fossil fuel emissions. However, Americans seem not to be actively engaged in this matter. For its handling climate change issues, the Bush Administration has been ridiculed more than any other government. This situation provides an opportunity for us to re-evaluate science on climate change.

The current state of science regarding climate change is influenced by many factors. These include the Bush Administration's use of uncertainty in describing the threat of climate change and the role that synecdoche plays in the discourse. Synecdoche is a kind of rhetorical strategy that reduces key elements of a problem to an indeterminable whole. The result is that essential aspects of climate changes are suppressed.
Synecdoche is an important rhetorical resource. It is capable subordinating the irony to create comfort. It can be used to solve a problem, such as the irony and uncertainty. However, synecdochic reasoning that is not correct can remove the most important parts of a problem. UCS's discourse on global climate changes tries to connect the many parts of the problem to an interconnected whole.
The UCS discourse on global warming tries to decrease the power of uncertainty by emphasizing the interconnectedness of the parts and the whole. The Bush Administration's uncertainty encourages complacency, inertia and complacency. These attitudes are reinforced because of the uncertainty that the Bush Administration has created. This increases the conflict between people who are reasonably certain about climate change and those who aren't. Accordingly, Bush Administration's discourse regarding global climate changes is a form if discursive construction that emphasizes and questions scientific consensus.
The relationship between UCS/Bush Administration is not a synecdoche. Although the synecdoche of the UCS is based on the assumption that uncertainty is the main factor in the climate change problem, the Bush Administration has constructed uncertainty in a way that is not compatible with the ideal synecdoche. In fact, the Bush Administration's portrayal uncertainty strengthens inertia in order to combat climate change.
The UCS's method of exposing the Bush Administration's use of science to discuss global climate change is powerful. The UCS's discourse not only dissociates itself from the Bush Administration’s construction of uncertainty but also provides a synecdoche model to show how to reframe climate change discourse.
UCS's analysis on the Bush Administration's use of uncertainty is a great example of how to reframe complex problems by looking at the rhetorical strategies used in global climate change discourse. It is possible to identify how to avoid the rhetorical trap that leads to faulty synecdochic reasoning by analysing the Bush Administration's use synecdoche.
FAQ
What is climate change and how does it occur?
Climate change is the long-term shift in global weather patterns caused by an increase of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat and cause global temperatures to rise, which can lead to a variety of changes in weather patterns and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. These include burning fossil fuels, transporting electricity, cutting down trees, and farming livestock. When these activities release massive amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere it warms the planet at a much faster rate than natural processes like volcanic eruptions as these activities produce many times more emissions than volcanoes.
Deforestation also plays a large role contributing about 15-20% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Trees are destroyed or burned to release their carbon dioxide. Furthermore, forests act like a natural carbon sink and remove CO2 from air. Without this absorption capacity carbon dioxide levels will continue rising with devastating consequences to ecosystems all over the world.
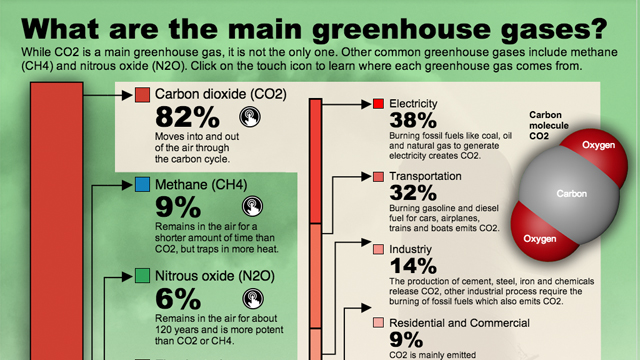
The release of CO2 into the atmosphere is not the only effect of human-caused polluting. Other harmful gasses like methane, CH4, and nitrous dioxide (N2O), are also emitted by humans. Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
The collective efforts of social, economic and political institutions must be made to drastically reduce the emissions and shift away from fossil fuel dependence. A smart approach to reducing atmospheric contamination and preventing CO2 accumulation could be to replace polluting fossil-fuel technologies with ones that encourage zero-waste living. Reforestation projects, which are powerful aid in the fight against climate change by absorbing large quantities of CO2 back into nature and maintaining biodiversity, can help us take responsibility for our environmental impact.
What are the impacts of climate change and global warming on agriculture and food security
Global warming and climate change are having a direct effect on food security and agriculture. The changing climate can affect rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels, and extreme weather. This can cause disruptions in farming, decrease crop yields, and result in a loss of agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures may lead to an increase in pests and diseases that can affect crops. They can also result in shifts of ranges suitable to agricultural production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels present a new threat. They can inundate agricultural land in many coastal locations, leading to increased salinity in wetlands where important crops grow. Climate change can also impact livestock production. Warm summer temperatures can reduce the fertility of animals like cows, sheep, and goats. This can cause lower milk yields and increase food insecurity within communities.
Global warming and climate change have a complicated relationship. However, adaptation strategies are being implemented by governments globally through strategic investments made in climate-smart farming (CSA). This involves promoting sustainable methods such as crop rotation techniques or genetic diversity through the conservation of native seed varieties, which help protect against negative impacts from extreme weather conditions or other environmental stressors caused by the changing climate. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
Farmers around the globe must adopt technology that is more sensitive to climate changes to ensure food security in a changing environment. Infrastructure must be improved so that the necessary actions can be taken when critical crop thresholds have been reached. This includes creating stable irrigation networks with adequate water supply at times when water is scarce or when temperatures rise. Collaboration between different stakeholders is needed to ensure that the quality nutrition guidelines are adhered to in all climates.
How can the planet move toward a more sustainable world in the face of climate change-related challenges?
Sustainability is the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. An urgent need exists to act to eliminate our dependency on finite natural resources and to shift towards a more sustainable method of using them.
It is crucial that we reexamine our consumption and production patterns, as well our dependence on fossil fuels, in order to move towards a sustainable future. We must search for new technologies, renewable energies, and systems to reduce harmful emissions, while still meeting our daily requirements.
In addition, it is essential that we adopt an integrated approach when looking at sustainability. This includes all aspects of production including materials, waste management and reuse strategies as well as energy usage in transport and industry. There are many potential solutions available including the utilization renewable energies like sun, wind, and water power; improved waste management systems; higher efficiency in agriculture; improved transport network; green building regulations; sustainable urban planning initiatives.
To achieve this goal, we need to make behavioral changes in order for people from all walks of society to be successful. Education programs are necessary to help people understand the climate change issues and how they can make a positive contribution towards a more sustainable world.
Collaboration between government leaders, industry leaders, as well as citizens is the only way to make significant progress toward creating a more sustainable future for our children.
Is there any potential for new technologies that address climate change?
This global problem is a huge challenge that new technologies can address. We can now transition to a more sustainable tomorrow by utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and geothermal, as well energy storage systems like thermal tanks or battery packs.
Carbon capture and sequestration are two methods that can be used to lower greenhouse gas levels. Enhanced agricultural practices can reduce livestock emissions and soil degradation. Smart grid technology may also be used to boost efficiency and improve building design.
In addition, cutting-edge synthetic biology approaches allow scientists to develop organisms that can utilize green sources of fuel such as CO2 laser into usable biofuel or alternate feedstock. This could revolutionize transportation if the market turns away from petrol-based vehicles toward zero-emission electric cars powered by clean sources.
Finally, increasing investment in digital tech and AI can enable people to access data across borders and help them make more informed consumption decisions. Understanding how we contribute to the carbon production of our planet is key for better stewardship.
What are the impacts of climate change on society and the environment?
Climate change has many impacts on society and the environment. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate change is having an enormous impact on the environment as well as societies around the globe. Global temperatures are expected to continue to rise and this will only get worse in the future.
One of the most widespread effects of climate change is the rising ocean levels due to melting of ice caps. This can lead to shoreline erosion and increased flood risk for coastal communities. In many countries, saltwater intrusion can also occur, affecting freshwater supplies in the coastal areas.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
The increasing frequency of wildfires that are caused by climate change has also led to devastating consequences for both habitats and those living nearby.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. The possibility of pest infestations increasing is linked to increased temperature extremes, a phenomenon known "greenhouse bug". This further impacts global food insecurity. A smaller number of crops with lower nutritional quality could lead to additional hardships for those already struggling to make ends met.
How can climate change be mitigated or reduced in its impact?
There are many ways to reduce or mitigate the impact of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. It is important to increase public awareness about climate change as it makes people feel accountable for their actions.
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. In fact, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), humans are responsible for more than 70% of all global warming since the mid-20th century.
Carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels like oil, coal, and gas. This will increase the atmospheric CO2 levels already present. It acts as a "greenhouse gases" by trapping heat in Earth's atmosphere, increasing temperatures even more. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Trees that sequester atmospheric CO2 in their trunks during photosynthesis are destroyed by deforestation. Also, cutting down forests can increase albedo - which is the amount reflected solar radiation going back into space. It also reduces solar heat absorbtion by the earth's surfaces and encourages excessive global warming. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more efficient and fight climate change
Your home's energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective ways to cut your carbon footprint, lower your utility bills, and improve your quality of life.
Your home should be properly sealed and insulated. You must ensure that your windows and doors fit properly. If you find drafts around pipes or vents, make sure to add weather stripping and fill in any gaps with caulking around door frames and window frames.
Insulate your walls, ceilings, and floors to maximize energy efficiency. Check for air leaks in the attic or other areas of your home that are not well-insulated.
Lighting is responsible for 18% of household electricity use. LED bulbs are up to 80% more efficient than traditional incandescent light bulbs. Additional money can be saved by installing motion sensors, timers, and turning off lights only when needed.
An old boiler or furnace can be replaced to save money on energy. They are also more efficient. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
All windows should be replaced by double-glazed units that are more energy efficient and less heat escaping. Look into buying low-flow showerheads which reduce water consumption while maintaining adequate pressure levels.
ENERGY STAR rated devices use 50 % less energy than non-certified appliances. Do not forget to unplug electronic devices, such TV boxes or phone chargers, when not in usage. This can help you save considerable energy.
These are just a few of the steps that can dramatically reduce your impact on climate change and lower monthly electricity bills, making it easier to live at home.