
Europeans are concerned about climate change in many ways. They range from personal impacts to environmental damage. There is a strong feeling that the world is warming and extreme weather events are increasing. Despite these challenges, the European Union has committed to decarbonizing and has promised to meet its 2050 goal. However, the region faces challenges in a rapidly changing global policy environment. Europe is also vulnerable to the worst impacts of climate change.
Many countries across the region will be affected by climate change. Germany, for example, has a large number of people who are concerned about this issue. The country also produces the second largest amount of coal in EU, behind Poland. Despite its large coal production, the country has struggled to decrease it.

The EU biodiversity strategy forms part of the European Green Deal. It is a part of a commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decarbonize. It also calls for a 50% drop in pesticide use by 2030. It calls for the restoration of 25,000 km of Old-growth forests and rivers.
Young adults, particularly those between the ages of 18 and 29, are more concerned about climate change's personal impacts. This is especially true in Sweden. At least 40% of young Swedes are very concerned about the potential harm from climate change.
Protests against climate change are being led by young people. For instance, the Swedish youth climate activist Greta Thunberg is a leading force in Europe. Sweden has a higher percentage of adults concerned about the effects of climate change than other nations.
Young adults are more concerned about the effects of climate change on global ecosystems. Besides, they are also more likely to change their lifestyles in response to the problem. The United States also has a large gap between the ages of older and younger Americans, with the oldest being more concerned about global climate change than those who are younger.
A recent study showed that the level of concern about climate change was rising across the EU. Nearly every country with trend data has seen a significant increase in the number of very concerned citizens. Australia, Japan (and Spain) are among the countries with double-digit increases of concern.
Europe's poorest populations will be among the most affected by climate change. These countries are often the first ones to be affected by extreme weather conditions like heatwaves and floods. Moreover, the increased frequency of such events may increase the severity of diseases in humans and animals.
The European Union has set aside 25% of its budget for fighting climate change. A large part of this budget will be spent on nature-based solutions and restoring biodiversity. The European Commission launched a biodiversity strategy to combat climate change. The strategy calls, among others, for the restoration 25,000 kilometers of rivers as well as a 50% decrease in pesticide use.
FAQ
What is the current global climate? And how is it changing over time?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes are already having a profound affect on ecosystems worldwide, causing extinctions or disruptions of habitats. They are also threatening lives and livelihoods for billions of people, especially those who live in areas with resource scarcity.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. This trend will continue as temperatures continue rising.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also creating social inequalities bydisproportionately affecting marginalized populations that don't have the knowledge and resources necessary to adapt.
While some countries have made progress in reducing carbon emissions, or implementing renewable energy initiatives, global action has not been taken at the level necessary to combat these changes. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. The political stances taken by different actors will impact the implementation measures to combat climate changes. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
In particular, various governments around the world are keen to protect their economic interests and enforce measures that would limit business activities as little as possible; this frequently conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend for addressing climate change in an efficient manner. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
Different power dynamics can make it difficult to achieve full consensus on the best ways to address climate change. Countries with more economic power may appoint themselves to be represented on international bodies for negotiations about the environment. This can lead the to divisive discussions between the countries' interests and the collective interest. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change is due in large part to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. (IPCC), human activity is responsible for more that 70% of all global warming.
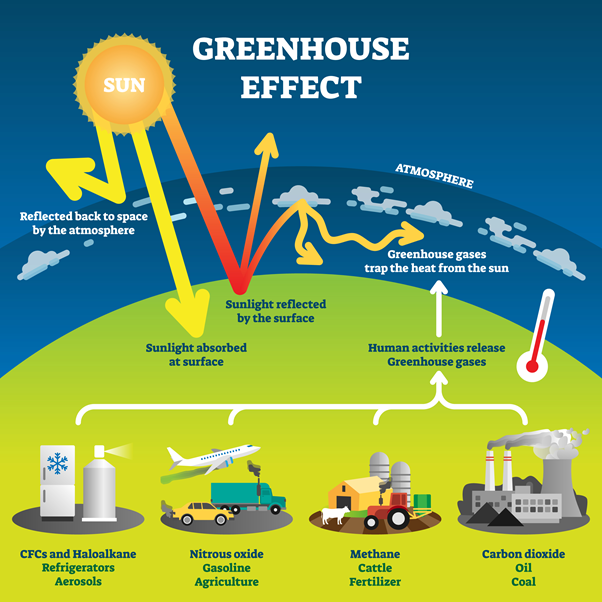
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This will increase the atmospheric CO2 levels already present. It acts as a "greenhouse gases" by trapping heat in Earth's atmosphere, increasing temperatures even more. This causes higher ocean levels, as Arctic ice melts. It also scrambles weather patterns across the globe, leading to dangerous storms, droughts, floods and other problems that can affect food production and human health.
Deforestation is the removal of trees that store atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks. This happens when they use it during photosynthesis. The albedo is also increased by cutting down forests. It refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected back into space. The deforestation of forests can also affect the local air quality, which is directly linked to respiratory problems.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Because animal waste is rich in methane bacteria, large amounts of methane are released into the atmosphere. This can lead to a significant increase in global warming.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
Statistics
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest In Clean Energy and Support the Transition To A Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy refers to any type of renewable energy that does no polluting or emit carbon dioxide, as well as other greenhouse gases. It can include technologies such as solar photovoltaics, wind power and hydroelectricity. Renewable energy sources have many environmental benefits. This includes a decreased reliance on fossil oil, a decrease in air pollution caused by traditional electricity methods, as well as providing reliable electric access to remote locations.
Shares in companies developing innovative technologies in clean energy can be purchased by investors. This includes investing in publicly traded stocks, mutual funds and ETFs (exchange traded funds) that are related to renewable energy. Investors might also consider direct investments in start-ups or venture funds to finance research and development for clean technology technologies.
Investors who invest in clean energy are supporting innovation that helps reduce harmful emissions from traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. The tax incentives programs that encourage investment into green technologies such as wind farms and solar panels can also provide investors with a financial reward.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.