
The climate system includes a number of positive and negative feedbacks. A key component of the climate system are the feedbacks. They counteract the effects caused by climate forcing. The change in radiative emissions is one common indicator of the effectiveness of a feedback. These measurements are called feedback parameters. These measures are useful when assessing the potential climate change resulting from a perturbation.
For example, the carbon climate feedback parameter g (carbon-climate feedback) is a measure the relative influence of a warming top on land carbon inventories. This is an important measure because it indicates the extent to that a warmer environment alters the land's carbon contents. However, it is not a comprehensive measure for the climate feedback.

Similar to the carbon-climate feedback parameter (b), the carbon concentration feedback parameter (c) measures how much an increase in atmospheric CO2 concentration increases ocean CO2 uptake. Unlike the carbon-climate feedback, b is a function of both land and ocean CO2, but the magnitude of b is smaller when the CO2 concentration is greater.
Another example of feedbacks is the cloud and sea-ice feedbacks. Both of these processes affect the polar regions. They are relatively weaker in polar areas than in the tropics, but they are still important. These interactions can be simulated by climate models. These processes can also be estimated using observations.
The largest water vapour feedbacks occur in the tropics where an increase of water vapor strengthens the initial heat source. Water vapour is a greenhouse gas that increases the planet's temperature. Additionally, an increase of water vapour leads to an increase in ocean temperature. For geological events, some of these feedbacks were studied in depth.
The ice production-ocean heat storage feedback is a relatively small measure of the effect of climate change on the storage of thermal energy. This measurement is reasonable because an increase in heat losses results in an increase in the amount of heat stored. This effect can also be quantified in many different ways. It is helpful for understanding the mechanisms of climate changes.
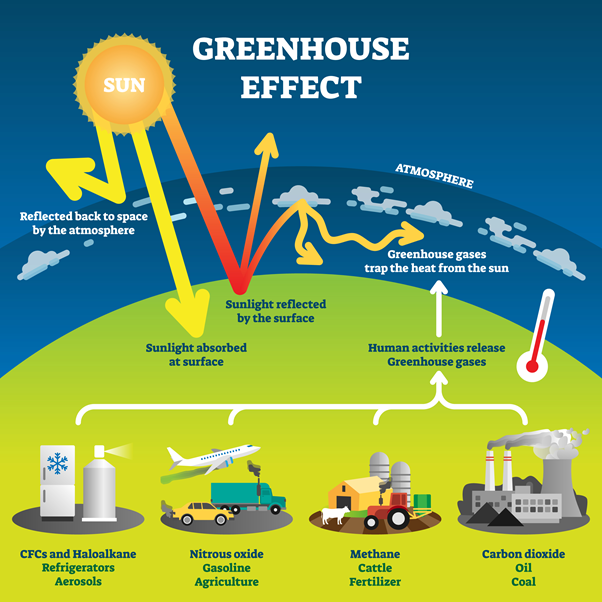
Another important component of climate system is carbon-cycle feedbacks. They are linked to the changes in land and ocean carbon inventories. These parameters can generally be identified by comparing differences within model simulations that have been constrained with observations. These parameters should not be compared for the exact same scenario. Nevertheless, the differences in model outputs are quite significant, and the uncertainties are often large.
The range between two and five K is where the best estimates of total Feedback are. Although they are not perfect, these estimates are close. These are the best known equilibrium temperature changes. They can be adjusted to account for 3.5W m-2 additional CO2. The expected equilibrium temperature variations range from 2 - 5.8 K. So, the standard radiative response framework is a good estimate. These parameters will need to be adjusted for non-radiative effects such as land and ocean condensation and evaporation.
FAQ
How can the impact of climate change be reduced or mitigated?
There are many things you can do to lessen and mitigate the consequences of climate changes. These include reducing greenhouse gases emissions by using better energy practices and other sources of electricity, improving land management, protecting forests and wild places, protecting against extreme weather, investing in sustainable transport, strengthening early warning system for disasters, starting a research programme on the impact climate change has on biodiversity and ecosystems. Also investing in green technologies like solar cells or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consume habits, and implementing environmental regulations across all segments of society. It's important that people are educated about climate change. This encourages them to take responsibility for their actions.
What is the contribution of human activity to climate change?
Climate change is a major contributor to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Changes (IPCC), more than 70% global warming has been caused by humans since the middle of the 20th century.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This will increase the atmospheric CO2 levels already present. It acts as a "greenhouse gases" by trapping heat in Earth's atmosphere, increasing temperatures even more. This causes higher ocean levels, as Arctic ice melts. It also scrambles weather patterns across the globe, leading to dangerous storms, droughts, floods and other problems that can affect food production and human health.
Deforestation - Trees which store atmospheric carbon dioxide within their trunks, when they absorb it through photosynthesis, are removed by deforestation. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Animal agriculture accounts for between 14%-18% worldwide's total anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
Conclusion: Human activity has had a profound impact on the environment for centuries. However, technology has made it possible to leverage green innovation and make eco-friendly efforts to combat climate change. This will ensure that everyone is safe while prospering in nature.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
The environment and society are both affected by climate change. Climate change is causing a variety of environmental problems, including rising temperatures, extreme weather, sea level rise, and reduced air quality. These changes can have severe consequences for human populations. They can lead to instability, increased poverty, insect-borne diseases and altered migration patterns.
Already, climate change has had a broad range of devastating effects on society and the environment around the globe. As global temperatures continue to rise, this is likely to worsen in the near future.
Ocean levels rising due to melting ice caps is one of the most pervasive effects of climate change worldwide. This leads to shoreline erosion at many coasts as well as an increased risk for flooding for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Extreme weather events such as heatwaves and droughts regularly occur across many countries around the world as a result of climate change. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Also, wildfires due to climate change are occurring more often than ever. These fires can cause severe damage to habitats and the lives of people living close by.
These drastic changes often lead to displacement or refugee crises. People move out of their homes involuntarily or voluntarily when their communities become unsafe or uninhabitable due to the altered climate.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. The possibility of pest infestations increasing is linked to increased temperature extremes, a phenomenon known "greenhouse bug". This further impacts global food insecurity. A smaller number of crops with lower nutritional quality could lead to additional hardships for those already struggling to make ends met.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more efficient and fight climate change
It is possible to make your home more energy efficient, reduce your carbon footprint and save money on your utility bills.
Start by ensuring your home is properly insulated and sealed. Check for drafts, ensure doors and windows are properly installed, and then seal any gaps or cracks with caulking.
To maximize energy efficiency, insulate your ceilings, walls, and floors. Make sure to inspect the attic and any other areas in your home for air leaks.
Lighting accounts for approximately 18% household electricity consumption. You should switch to LED lights, which use as little as 80% of traditional incandescent lamps. You can also save money by installing motion sensors and timers to turn off lights when they are not needed.
A newer model is more efficient and can help reduce your energy bills. Get a programmable thermostat to adjust the temperature depending on whether people are at home or not.
Double-glazing windows can be replaced with better insulation. They also prevent heat from escaping through the glass. Low-flow showerheads are a great option, as they reduce water consumption but maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated items can be used to replace appliances that consume up to 50% less power than noncertified models. You can save a lot of energy by not plugging in electronic devices such as TV boxes or phone chargers when they are not being used.
These are just a few of the steps that can dramatically reduce your impact on climate change and lower monthly electricity bills, making it easier to live at home.